Reading--Notes
HTML
Heading
Heading in HTML :
HTML has six “levels” of headings :
h1 is used for main headings and h2 is used for subheadings If there are further sections under the subheadings then the h3 element is used, and so on..

Paragraph
To create a paragraph, surround the words that make up the paragraph with an opening tag and closing tag.

Bold & Italic
we can make the text bold by enclosing words in the tags we can make characters appear bold. and for italic By enclosing words in the tags <i </i> we can make characters appear italic.

Superscript & Subscrip
The sup element is used to contain characters that should be superscript such as the suffixes of dates or mathematical concepts like raising a number to a power such as 22.
The sub element is used to contain characters that should be subscript. It is commonly used with foot notes or chemical formulas such as H20
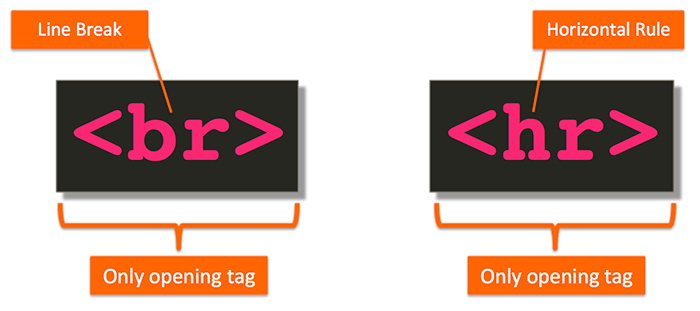
Line Breaks & Horizontal Rules
br : As you have already seen, the browser will automatically show each new paragraph or heading on a new line. But if you wanted to add a line break inside the middle of a paragraph you can use the line break tag.
hr : To create a break between themes — such as a change of topic in a book or a new scene in a play — you can add a horizontal rule between sections using the hr tag.
Strong & Emphasis
The use of the strong element indicates that its content has strong importance. For example, the words contained in this element might be said with strong emphasis.
The em element indicates emphasis that subtly changes the meaning of a sentence.
Quotations
- There are two elements commonly used for marking up quotations:
-
blockquote : is used for longer quotes that take up an entire paragraph. Note how the p element is still used inside the blockquote element.
-
q : is used for shorter quotes that sit within a paragraph. Browsers are supposed to put quotes around the element, however Internet Explorer does not — therefore many people avoid using the
element.

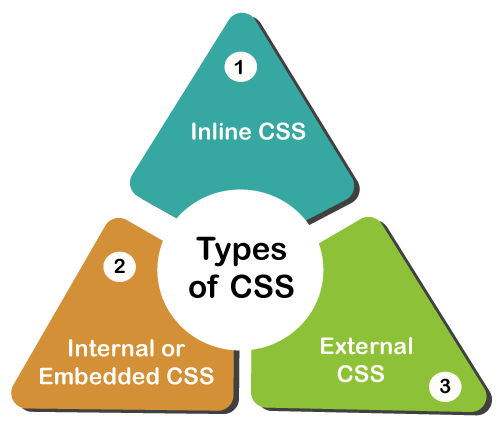
css
CSS allows you to create rules that control the way that each individual box (and the contents of that box) is presented.

Example Styles :
- Boxes : Width and height Borders (color, width, and style) Background color and images Position in the browser .
- Text : Typeface ,Size, Color, Italics, bold, uppercase, lowercase, small-caps.
- Specific :There are also specific ways in which you can style certain elements such as lists, tables, and forms.
- Using External CSS :
Link element can be used in an HTML document to tell the browser where to find the CSS file used to style the page. It is an empty element (meaning it does not need a closing tag), and it lives inside the head element.
It should use three attributes:
- href : This specifies the path to the CSS file (which is often placed in a folder called css or styles).
- type : This attribute specifies the type of document being linked to. The value should be text/css.
- rel : This specifies the relationship between the HTML page and the file it is linked to. The value should be stylesheet when linking to a CSS file.

- Using Internal CSS :

### Why use External Style Sheets?
When building a website there are several advantages to placing your CSS rules in a separate style sheet. All of your web pages can share the same style sheet. This is achieved by using the element on each HTML page of your site to link to the same CSS document. This means that the same code does not need to be repeated in every page (which results in less code and smaller HTML pages).
JavaScript
STATEMENTS :
A script is a series of instructions that a computer can follow one-by-one. Each individual instruction or step is known as a statement. Statements should end with a semicolon.

COMMENTS :
You should write comments to explain what your code does. They help make your code easier to read and understand. This can help you and others who read your code.

WHAT IS A VARIABLE?
A script will have to temporarily store the bits of information it needs to do its job. It can store this data in variables. When you write JavaScript, you have to tell the interpreter every individual step that you want it to perform. This sometimes involves more detail than you might expect.

Rules For Naming Varibles :
-
The name must begin with a letter, dollar sign ($),or an underscore (_). It must not start with a number.
-
The name can contain letters, numbers, dollar sign ($), or an underscore (_). Note that you must not use a dash(-) or a period (.) in a variable name.
-
You cannot use keywords or reserved words. Keywords are special words that tell the interpreter to do something. For example, var is a keyword used to declare a variable. Reserved words are ones that may be used in a future version of JavaScript. ONLINE EXTRA View a full list of keywords and reserved words in JavaScript.
-
All variables are case sensitive, so score and Score would be different variable names, but it is bad practice to create two variables that have the same name using different cases.
-
Use a name that describes the kind of information that the variable stores. For example, fi rstName might be used to store a person’s first name, l astNarne for their last name, and age for their age.
-
If your variable name is made up of more than one word, use a capital letter for the first letter of every word after the first word. For example, f i rstName rather than fi rstnarne (this is referred to as camel case). You can also use an underscore between each word (you cannot use a dash).
ARRAYS :
An array is a special type of variable. It doesn’t just store one value; it stores a list of values.

EXPRESSIONS :
An expression evaluates into (results in) a single value. Broadly speaking there are two types of expressions.
OPERATORS:
Expressions rely on things called operators; they allow programmers to create a single value from one or more values.

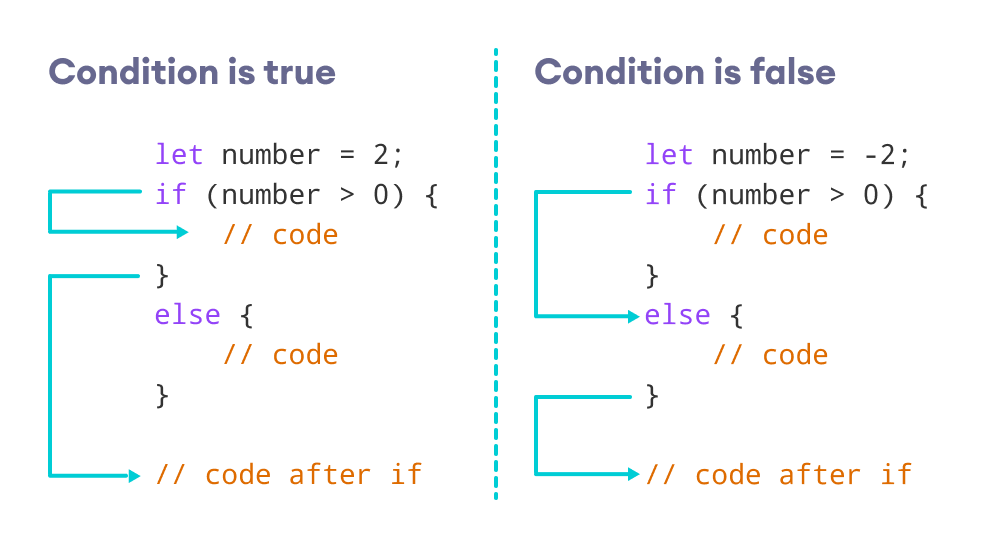
If Statements :
the IF statement evaluates or checks a condition. if the condition evaluate to true , any statements in the subseguent code block are executed.
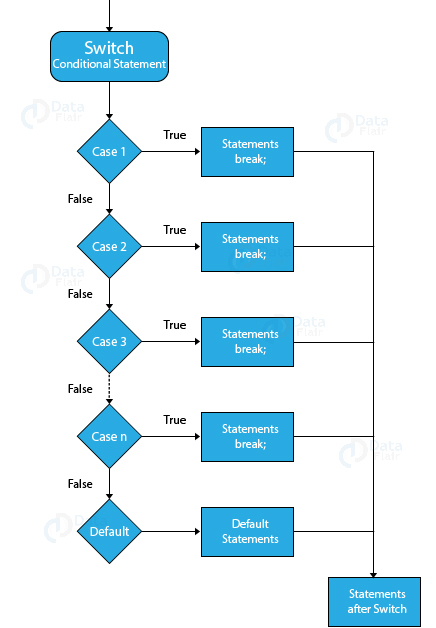
## Switch Statements : Its a statement starts with a variable called the switch value. each case indicates a possible value for this variable and the code that should run if the variable matches that value.