Reading--Notes
HTML
Introduction
First how people access the web ?
-
** Browsers** : People access websites using software called a web browser. Popular examples include Firefox, Internet Explorer, Safari, Chrome, and Opera.
-
Web Servers : When you ask your browser for a web page, the request is sent across the Internet to a special computer known as a web server which hosts the website.
-
Screen Readers : Screen readers are programs that read out the contents of a computer screen to a user. They are commonly used by people with visual impairments.
-
Devices: People are accessing websites on an increasing range of devices including desktop computers, laptops, tablets, and mobile phones. It is important to remember that various devices have different screen sizes and some have faster connections to the web than others.
Structure
How pages use structure?
think about the stories you read in a newspaper: for each story, there will be a headline, some text, and possibly some images. If the article is a long piece, there may be subheadings that split the story into separate sections or quotes from those involved. Structure helps readers understand the stories in the newspaper.
The structure is very similar when a news story is viewed online (although it may also feature audio or video). This is illustrated on the right with a copy of a newspaper alongside the corresponding article on its website.
HTML uses elements to describe the structure of pages , see the example below :

Tags act like containers. They tell you something about the information that lies between their opening and closing tags.
here a closer look at tag :
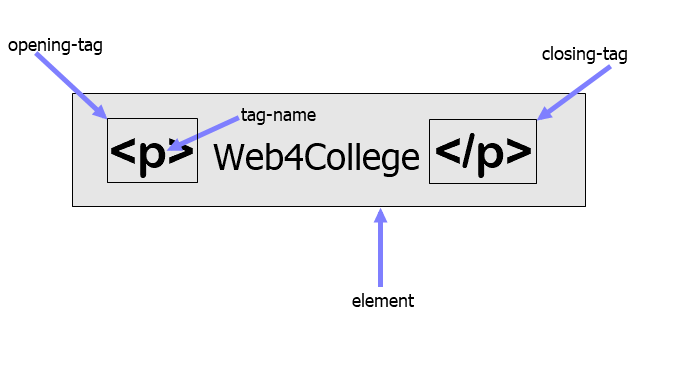
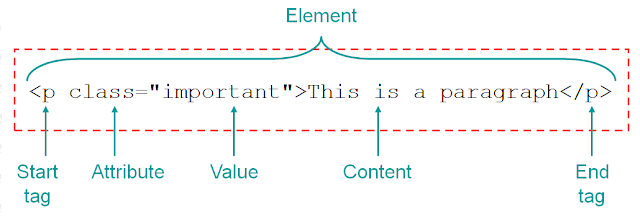
Attributes : Attributes tell us more about eLements its provide additional information about the contents of an element. They appear on the opening tag of the element and are made up of two parts: a name and a value, separated by an equals sign.
here an example :
Extra Markup
- DOCTYPES : tell browsers which version of HTML you are using.
- You can add comments to your code between the markers.
- The id and class attributes allow you to identify particular elements.
- The <div> and **** elements allow you to group block-level and inline elements together.
- **
** cut windows into your web pages through which other pages can be displayed. - The tag allows you to supply all kinds of information about your web page.
- Escape characters are used to include special characters in your pages such as <, >, and ©.
Here is a (html code) like an example about what we mention before:
# HTML5 Layout
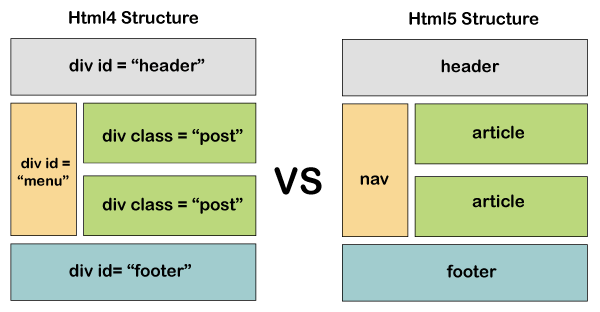
See the image below that describe the different between Traditional HTML Layouts and the New Html5 Layout Elements :
-
The new elements provide clearer code (compared with using multiple <div> elements).
-
Older browsers that do not understand HTML5 elements need to be told which elements are block-level elements.
To make HTML5 elements work in Internet Explorer 8 (and older versions of IE), extra JavaScript is needed, which is available free from Google.
### Here is some new elements in HTML5 :
- Headers & Footers.
- Navigation.
- Navigation.
- Article.
- Sections.
- Heading Groups.
- Figures.
- Sectioning Elements.
Process & Design
Who is the site for?
Every website should be designed for the target audience—not just for yourself or the site owner. It is therefore very important to understand who your target audience is.
Why people visit your website?
Now that you know who your visitors are, you need to consider why they are coming. While some people will simply chance across your website, most will visit for a specific reason.
What your visitors are trying to achieve?
It is unlikely that you will be able to list every reason why someone visits your site but you are looking for key tasks and motivations. This information can help guide your site designs.
What information your visitors need?
You know who is coming to your site and why they are coming, so now you need to work out what information they need in order to achieve their goals quickly and effectively.
How often people Will visit your site?
Some sites benefit from being updated more frequently than others. Some information (such as news) may be constantly changing, while other content remains relatively static.
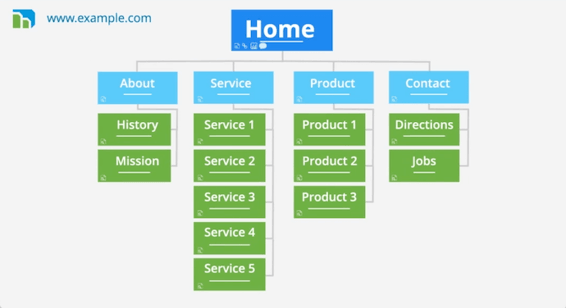
Site Maps :
Now that you know what needs to appear on your site, you can start to organize the information into sections or pages.
example site map :
WireFrames:
A wireframe is a simple sketch of the key information that needs to go on each page of a site. It shows the hierarchy of the information and how much space it might require.
Example Wireframe :

Getting your message across using design :
The primary aim of any kind of visual design is to communicate. Organizing and prioritizing information on a page helps users understand its importance and what order to read it in.
Visual Hierarchy :
Most web users do not read entire pages. Rather, they skim to find information. You can use contrast to create a visual hierarchy that gets across your key message and helps users find what they are looking for.
Grouping and Similarity :
When making sense of a design, we tend to organize visual elements into groups. Grouping related pieces of information together can make a design easier to comprehend. Here are some ways this can be achieved.
Designing Navigation :
Site navigation not only helps people find where they want to go, but also helps them understand what your site is about and how it is organized. Good navigation tends to follow these principles…
JavaScript
Introduction
JavaScript can be used in browsers to make website more interactive.

Whats a script and how do I craete one?
-
A script is a series of instructions that the computer can follow in order to achieve a goal.
-
Each time the script runs, it might only use a subset of all the instructions.
-
Computers approach tasks in a different way than humans, so your instructions must let the computer solve the task prggrammatically.
-
To approach writing a script, break down your goal into a series of tasks and then work out each step needed to complete that task (a flowchart can help).
How do I wrie a script for a web page?
-
It is best to keep JavaScript code in its own JavaScript file. JavaScript files are text files (like HTML pages and CSS style sheets), but they have the . j s extension.
-
The HTML
-
If you view the source code of the page in the browser, the JavaScript will not have changed the HTML, because the script works with the model of the web page that the browser has created.